Flow Meters
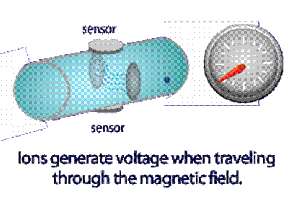
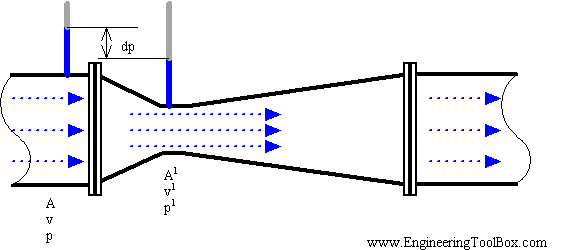
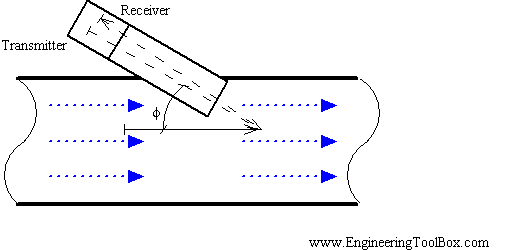
Flowmeters are used to measure the mass or volumetric rate of flow for a liquid or gas. Some flow meters are designed to measure the rate of flow through the flow meter for a time period, while others measure the actual mass or volume that has passed through. Those that measure rate of flow, such as magnetic and turbine flow meters, do so by measuring the velocity of the fluid through the flow meter to determine volumetric flow. The positive displacement flow meter, which directly measures volume, rapidly and repeatedly entraps the fluid to detect its flow, and then multiplies that by the cross-sectional area of the pipe (a constant factor of course) to determine total volume.
A standard flow meter consists of three main parts: a primary device, a transmitter, and a transducer. The fluid being analyzed by the flow meter passes through the primary device, where a readable flow signal is created from the transmitter from the one that is automatically sensed by the transducer.
Factors that should be taken into consideration when finding the right flow meter include:
- viscosity (resistance) of fluid - is it Newtonian or non-Newtonian?
- rate measurement
- sanitation of liquid (yes, they are labeled as “clean” or “dirty”)
- type of display on the flow meter (or external output?)
- maximum and minimum flow rates
- process pressure
- process temperature
- compatibility with other parts of the flow meter
- pipe size
- whether the information from the flow meter is needed locally or remotely
- material
- turns, regulators, valves
The following sources were used in compiling this general information on flow meters:
http://www.omega.com/prodinfo/flowmeters.html
To get an ideal flow meter for our design we will want something that has a digital display, is settable, and can send some sort of signal than can tell the pump when it should turn on and off. There exist such types of programmable, electronic flow meters, which can share transmissions with a certain data-update frequency, although they could be both hard to find and costly. More time and consideration should be taken into evaluating the installation of this flow meter. The following are just a few existing possible ideas:
However, what may be more practical is to use a simplistic type of flow meter and have it send an electronic signal to a device which can program when it should switch the different pumps on and off. The Modbus & Serial Output Transmitter may be one example of how this can be done. Otherwise we may try and create our own program through some sort of computer or arduino program for the purpose of saving time and money.
The following resources were also obtained, from Clark Solutions, and may prove to be valuable if future work is done in designing this system: